Globally, millions of people are affected by diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes. Despite its prevalence, many individuals remain uncertain about the intricacies of diabetes mellitus.
 |
| Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Symptoms, and Management |
This in-depth blog post explores the many forms of diabetes, as well as its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By understanding diabetes mellitus, you can make informed decisions to maintain your health and quality of life.
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Hyperglycaemia, or increased blood sugar, is a symptom of a set of illnesses known as diabetes mellitus that are caused by problems with insulin action, manufacturing, or both. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels and facilitating the entry of glucose into cells for energy.
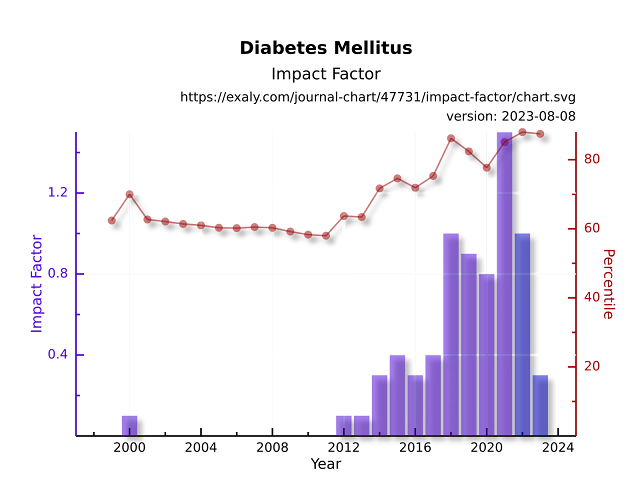
For the purpose of comparison with the full body of literature, the graph displays the changes in the impact factor of diabetes mellitus and its related percentile. The most popular scient metric statistic is called an impact factor, and it is calculated by dividing the total number of citations for two years prior by the total number of articles published in those years.
check the video below for more information
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common form of diabetes, typically occurring in adulthood. In this condition, the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, genetics, and advancing age. Symptoms may develop gradually and include increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, and slow wound healing.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Gestational diabetes mellitus occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes lead to insulin resistance. While the exact cause is not fully understood, hormones produced by the placenta interfere with insulin's action, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes typically resolves after childbirth, but affected individuals have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus later in life.
Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow wound healing
- Tingling or numbness in extremities
It's important to note that some individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus may not experience noticeable symptoms initially. Regular health check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection and proper management.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of diabetes mellitus are multifaceted and can vary based on the type of diabetes. For type 1 diabetes mellitus, genetic predisposition and environmental factors, such as viral infections, are believed to contribute to the autoimmune response. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is strongly associated with lifestyle factors, including obesity, sedentary behavior, and unhealthy dietary habits.Gestational diabetes mellitus is linked to hormonal changes during pregnancy. Other risk factors for diabetes mellitus include family history, ethnicity, advancing age, and certain medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or high blood pressure.
Preventing Diabetes Mellitus: Key Steps to Consider
While managing diabetes mellitus is essential, prevention is equally vital, especially for individuals at risk. Here are valuable steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing diabetes mellitus:
1 - Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus. By maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this form of diabetes. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight can have a positive impact on your insulin sensitivity.
2 - Adopt a Balanced Diet
Eating a nutrient-rich diet is a cornerstone of diabetes mellitus prevention. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods and limit the consumption of sugary beverages, refined carbohydrates, and high-fat foods. Make sure your diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
3 - Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Diabetes can be prevented with physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, coupled with strength training exercises. Regular physical activity not only helps with weight management but also improves insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health.
4 - Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
If you have a family history of diabetes or other risk factors, consider periodic blood sugar screenings. Early detection of elevated blood sugar levels can provide a window of opportunity to make lifestyle changes and prevent the progression of diabetes mellitus.
5 - Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of diabetes mellitus. Practice stress-relieving activities like yoga, deep breathing exercises, meditation, or spending time in nature.
6 - Get Quality Sleep
Get 7-9 hours of good sleep each night. Poor sleep patterns can disrupt hormones related to appetite and metabolism, increasing the risk of obesity and insulin resistance.
7 - Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can affect blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation, and always consider its impact on your overall health.
8 - Quit Smoking
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of diabetes mellitus, especially type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can not only reduce your risk but also improve your overall health.
9 - Regular Health Check-ups
Regular visits to your healthcare provider for routine check-ups can help you stay informed about your health status and identify any potential risk factors for diabetes mellitus.
10 - Diabetes Education and Support
Educate yourself about diabetes mellitus and its risk factors. Participate in diabetes education programs, workshops, and support groups to gain knowledge and connect with others who share similar health goals.
Conclusion: Understanding diabetes mellitus, its types, symptoms, and risk factors empowers you to take control of your health. Whether you're managing the condition or aiming to prevent it, making informed lifestyle choices is the key to a healthier life.
Remember that small changes can have a significant impact on your risk of developing diabetes mellitus. By adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce your risk and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Diabetes mellitus is a journey that requires dedication and commitment, but with the right knowledge and proactive steps, you can achieve better health outcomes and live a fulfilling life. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support on your path to diabetes prevention and management.

Comments
Post a Comment